Charles Dickens, the eminent Victorian novelist and social critic, was as much a product of his era as were his fictional creations. During his lifetime, Dickens amassed considerable wealth through his literary works, which include classics such as “A Christmas Carol,” “Oliver Twist,” and “Great Expectations.” His financial success was remarkable considering his humble beginnings and his challenges, including supporting an extensive family consisting of a wife, ten children, and a mistress post-separation from his wife.
By his death in 1870, Dickens’s net worth was significant enough to reflect his status as a leading literary figure. While the exact figures of his wealth may vary, it is clear that Dickens leveraged his talent to ascend the socioeconomic ladder—a journey mirrored by several of his characters. He strategically used the serialized novel format to generate a steady income and capitalized on the Victorian public’s appetite for his stories. His earnings enabled him to maintain a relatively comfortable lifestyle, a stark contrast to the financial hardship of his youth.
Content of This Article
- Charles Dickens’s Appearance
- Facts About Charles Dickens
- Charles Dickens’s Net Worth
- Early Life
- Charles Dickens’s Wife and Family
- Charles Dickens’s Career
- Charles Dickens’s Awards and Achievements
- Charles Dickens’s Controversies
Charles Dickens’s Appearance (Height, Hair, Eyes & More)
| Height |
6 ft 2 in
1.88 m |
| Weight |
167 pounds
76 kg |
| Hair Color | Salt and Pepper |
| Eye Color | Brown |
| Body Type | Average |
| Sexual Orientation | Homosexual |
Facts About Charles Dickens
| Nationality | Victorian |
| Estimate Net Worth | $1.5 million |
| Religion | Christian |
| Zodiac Sign | Aquarius |
| Birthplace | Portsmouth, England |
| Birthday | February 7, 1812 |
Charles Dickens’s Net Worth

As of 2023, Charles Dickens’s net worth was estimated at $1.5 million at his death in 1870—a significant sum for the period. As an author in the Victorian era, Dickens was highly prolific, creating some of his most memorable characters and stories. His work brought him unprecedented popularity, and by the early 20th century, he had earned recognition as a literary genius. The success of his novels, which include classics such as “Oliver Twist” and “A Christmas Carol,” contributed significantly to his wealth.
Addressing the difficulty in estimating the net worth of historical figures due to the time gap and changing economic value, some sources have tried to adjust Dickens’s wealth for inflation, which would substantially increase the figure by today’s standards. However, this estimation varies widely among scholars and economists. Throughout his career, Dickens managed to provide for his large family and enjoyed a lifestyle that reflected his success as an author.
Early Life
Born in Portsmouth, England, on February 7, 1812, Charles Dickens experienced financial hardship in his family from an early age. His father was often entrenched in debt, struggling to repay borrowed money, intimately shaping Dickens’s perspectives on poverty and financial management.
Education
Despite his family’s financial troubles, Dickens could attend the Giles Academy in Chatham in 1821 before moving to London, where he enrolled in Wellington House Academy. His academic pursuits were cut short at fifteen due to his family’s pressing economic needs. This adverse circumstance forced him back into the workforce, ending his formal education. However, it did not quench his thirst for knowledge, as he continued to educate himself through voracious reading.
Charles Dickens’s Wife and Family
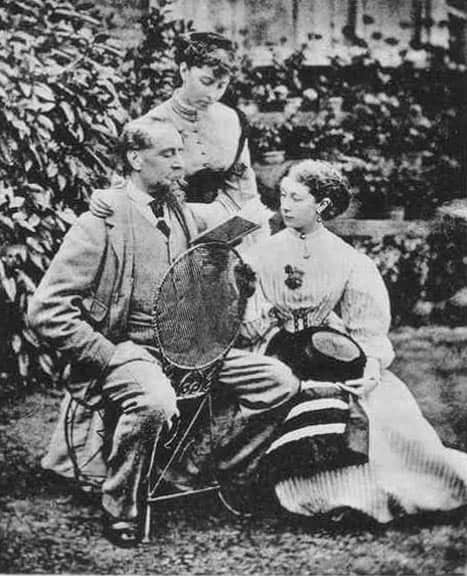
Charles Dickens’s private life was complex and fraught with personal challenges, which had significant implications for his family dynamics, particularly in his marriage and relationships with his children. Catherine Hogarth, who became Charles Dickens’s wife on April 2, 1836, was of notable family connection, being the daughter of George Hogarth, an editor for whom Dickens worked.
The couple’s life together began in the parish of St. Luke’s, Chelsea, and carried them through the joys of the early years of marriage, reflected by a honeymoon in Chalk, near Chatham. Their union produced ten children: Charles, Mary, Kate, Walter, Francis, Alfred, Sydney, Henry, Dora, and Edward. The family lived a comfortable life thanks to his literary earnings, marking the substantial familial responsibilities Dickens would bear throughout his lifetime.
Dickens’s care for his children was evident, but he also had high expectations, which not all could meet, leading to varied relationships and support. The divorce from Catherine did not just separate the couple but altered the dynamics within the Dickens family unit, with children often caught amid their parents’ estrangement. Catherine’s departure from the household precipitated a shift in care, as most of the children, excluding Charley, remained in their father’s custody alongside their aunt, Georgina Hogarth. This transition marked a significant change for the children and Catherine, who once held the role of mother and housekeeper for a sizable family.
Charles Dickens’s Career

Charles Dickens, an English writer and social critic, embarked on a literary journey that would solidify his status as one of the most influential novelists of the Victorian era. A prolific output of novels, journalistic works, and a pioneering role in serial publication distinguishes his career.
Early Works
Dickens’s writing career started with sketches under the pseudonym “Boz.” His initial work, “A Dinner at Poplar Walk,” was published in Monthly Magazine. These sketches were later compiled as “Sketches by Boz.” His knack for wit and social commentary was evident from the start.
Famous Novels
“The Posthumous Papers of the Pickwick Club” emerged from his early period, which brought him widespread acclaim. Dickens’s mastery of the novel form grew with each subsequent work. Iconic novels such as “Oliver Twist,” “David Copperfield,” and “Great Expectations” exhibit his sharp eye for social inequality and his compelling narrative techniques. His writing also reveals a blending of the real and the fanciful, canvasing both the bleak and the hopeful aspects of English society.
Journalistic Endeavors
Beyond novels, Dickens worked as a journalist and editor. He began his career as a political journalist for the Morning Chronicle, bringing attention to social issues. His editorial prowess was prominent in magazines like “Household Words” and “All the Year Round,” where he shared his critical observations of America and England.
Serial Publication
A novel feature of Dickens’s approach to literature was serialization. Serial publication of his works in magazines made them accessible to a broader audience. This method also allowed him to gauge reader response and sometimes alter his narratives accordingly. Dickens’s novels such as “Bleak House,” “Little Dorrit,” and “The Mystery of Edwin Drood” were published in installments, cementing the popularity of serial literature.
Charles Dickens’s Awards and Achievements

Despite his profound influence on Victorian literature and social reform, Charles Dickens was not recognized with awards. Most literary accolades we know today were established after his death. Excelling as a novelist, Dickens captivated audiences with his vivid characters and detailed depiction of Victorian society. His works sold extensively while being serialized and in complete book formats.
For his literary impact, he won a bestselling author award during the Victorian era, and his legacy includes continued readership and study of his works. For his posthumous recognition, his books remain literary classics, and adaptations of his works continue to receive awards.
Furthermore, for his notable posthumous award, Bleak House won the Audie Award for Literary Fiction & Classics in 2019. Lastly, for his cultural legacy, he’s now widely regarded as one of the greatest literary figures and is buried in the Poets’ Corner of Westminster Abbey.
By the time of his unexpected death from a stroke, Dickens had established an impressive estate, but he wasn’t commemorated through awards. Instead, he left behind a legacy recognized in the reform movements he supported and the literary masterpieces he created, which continue to be awarded and celebrated.
Charles Dickens’s Controversies

Charles Dickens, renowned for his literary contributions and social commentary, faced controversy concerning his views on colonialism and cultures outside of Europe. Regarded as a nationalist, Dickens often promoted European supremacy in his works and public statements.
One of his controversies is his cultural representation, wherein Charles depicted non-European societies using harmful stereotypes. He even labeled some cultures as “primitive” in his narratives, and this portrayal reflected a broader Victorian-era Eurocentric mindset.
Such controversy impacted his legacy in multiple ways, such as sparking debate on the implications for his legacy and scholars scrutinizing the intersection of his work with 19th-century colonial attitudes.
While not directly related to his net worth or the financial aspects of his estate, these controversies have influenced the posthumous perception of Dickens’ brand. Sales of his works and the management of his literary estate must navigate the complexities of his social views in modern interpretations and discussions.
Moreover, the value of Dickens’ estate at his death included proceeds from his prolific writing career. His sales and subsequent royalties were partly impacted by his standing with the public, which such controversies may have affected him. Controversies may also play a role in the ongoing financial management of his literary contributions.
In summary, Dickens’ controversial views on other cultures have become a point of examination and debate, influencing scholarly analysis and his literary estate’s continued financial viability.
Net Worth of Other Notable Authors
Isabel Allende’s Net Worth
Isabel Allende, a renowned novelist and one of the world’s most widely read Spanish-language authors, has accumulated considerable wealth throughout her illustrious career. Born in Lima, Peru, Allende has enthralled readers with her literary works, which often incorporate elements of magical realism. Her most famous novels include “The House of the Spirits” and “City of the Beasts,” which have garnered significant commercial success and critical acclaim. Her impact on literature extends beyond her narrative contributions; she has also been a significant influence in the cultural understanding and appreciation of Latin American storytelling traditions. As of 2023, Isabel Allende’s net worth is approximately $12 million.
Charlotte Bronte’s Net Worth
Charlotte Bronte, a prominent figure in 19th-century English literature, is celebrated for her enduring literary works, such as “Jane Eyre,” “Shirley,” and “Villette.” Born in 1816 in Thornton, Yorkshire, she emerged as a significant voice in Victorian literature, articulating deep psychological insight and exploring themes of social criticism and gender roles. Her novels, characterized by their complex characters and intricate narratives, continue to be widely read and appreciated, reflecting the challenges and the societal expectations of her time. Although Charlotte Bronte’s literary contributions are well-documented and her works continue to garner acclaim, specifics about Charlotte Bronte’s net worth at the time of her death remain less commonly known.